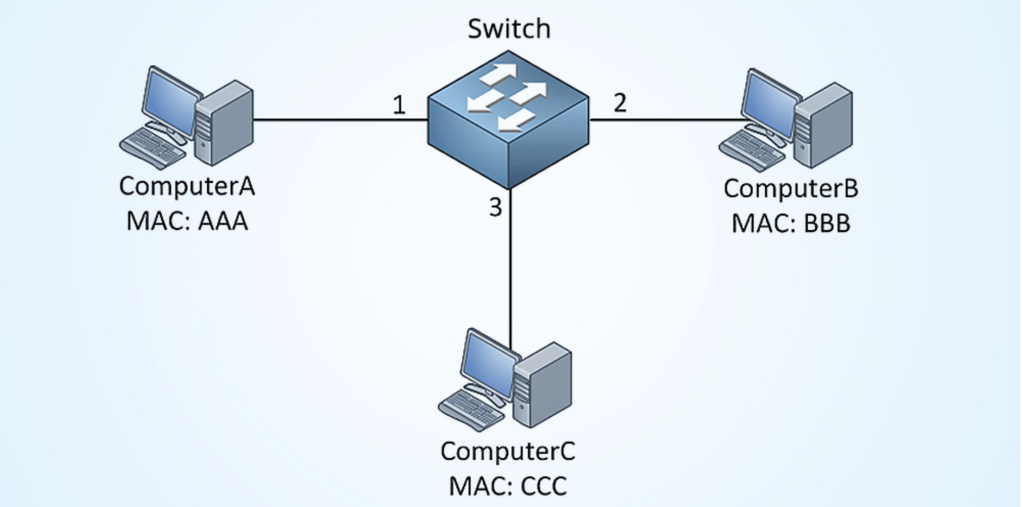
Physical Switch: When a switch is first powered on, the MAC address table is empty. The switch will build MAC address table and only learn from source mac address. Lets say there is switch with 3 servers connected to it. All the servers will have real mac address but for sake of explanation lets assume there mac address are AAA,BBB and CCC respectively ( screenshot below).
Server A is going to send some data to Server B. It will create a Ethernet Frame which has source MAC address (AAA) and destination MAC address ( BBB). The switch will build MAC address table and only learn from source MAC address. At this point, it just learned that MAC address of server A is on this interface and put that information in MAC address table. Since switch doesn’t know where server B , it has no option but to flood the frame to all the interface except from where it came from. Server B and C will receive the frame. Since Server B will see its MAC address as destination in the frame, it knows that frame is meant for him and Server C will discard it. Server B is going to respond to Server A, will build a frame with destination MAC address of A. At this point, switch will learn about MAC address and interface of Server B and will put it in MAC address table. That’s it, going forward any frame meant for server A or B will directly go to them. Server C will not see the frame except first time when switch flooded the frame on all its interface. One point worth mentioning that all mac address table uses an aging mechanism for its entries , so if MAC address of server A and B are not updated within its aging timer, they will be deleted.
VMware vSwitch : vSwitch doesn’t learn mac address from passing traffic. This goes for both standard and distributed vSwitch. It relies on the information that hypervisor( vmKernel) provides them about VM vNIC mac address. It knows that all vSwitch non uplink ports are used by VMs with known mac address. So a frame origination from a VM will be delivered to the right port if it is in the same vLAN and matches the destination mac address or send to the uplink. We can run the command “net-stats -l” from ESXi shell. This will print the mac address and port number of all the VMs on that ESXi host.